Relative clauses
The most important unit of grammatical organization in linguistics is the sentence. Second in importance is ‘the clause’ – and the best way to think about clauses is – as part of a sentence.
Relative clauses in advanced English are clauses that begin with the following relative pronouns
- who
- whom
- whose
- that
- which
- what
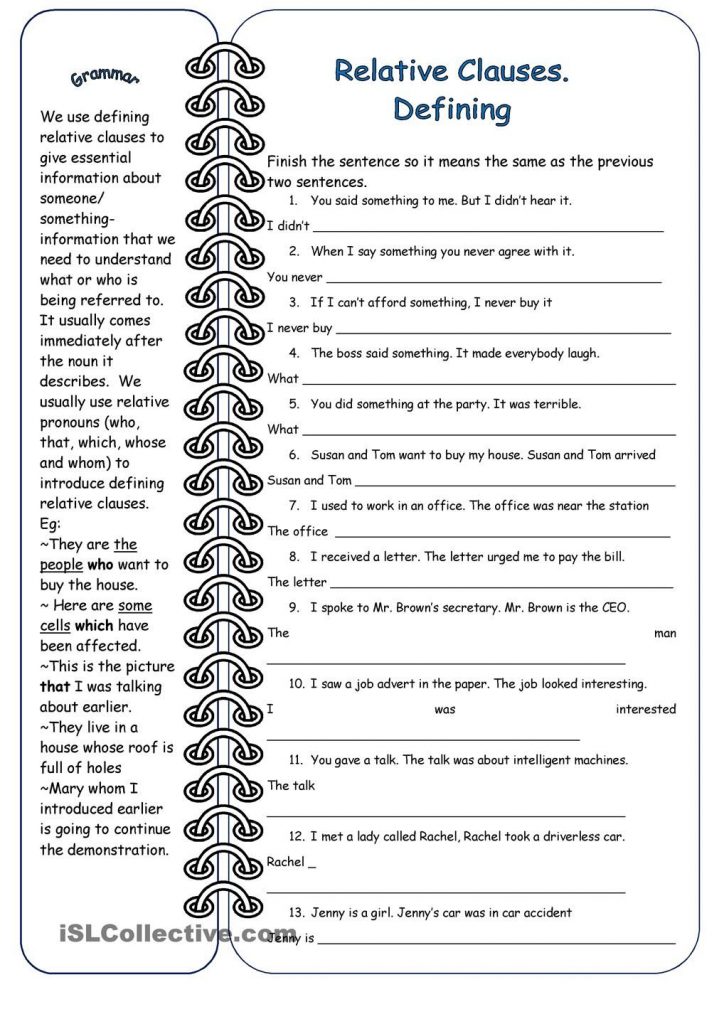
Defining Relative clauses
These type of clauses give essential information about a thing or person.
- This is the key which opens the door.
1. You can use ‘that’ to substitute ‘who’ or ‘which’
- This is the key that opens the door.
2. You use ‘whose’ for possesive clauses.
- That’s the guy whose son won the lottery.
3. If ‘who’ or ‘which’ are in fact the object of the verb then you can eliminate them.
- Messi is the player who I voted for.
- Messi is the player I voted for.
4. In dramatic, formal English, you use ‘whom’ (person) ‘which’ (thing) and you put the preposition before them. In informal English we usually eliminate the relative pronoun and put the preposition at the end.
- My boss is the mentor to whom I owe everything.
- My boss is the mentor I owe everything to.
5. ‘What’ is used as a relative pronoun to mean ‘the thing’ or alternatively ‘the things which.’ We also use this in the advanced English grammar construction known as cleft sentences.
- What I really want is world peace.
- He told me that what he really wanted was world peace.
Non-defining relative clauses
As the name suggests, a NDRC is a clause that provides supplementary information – not defining information.
1. When writing advanced English you must use commas or comma + fullstop to separate the clause.
- It was my ex-girlfriend, who was from Venezuela, that sold my car.
2. In non defining relative clauses you can not substitute ‘who/which’ for ‘that.’
- My ex was calling me all night, which was bloody annoying.
3. You can use ‘which’ to refer to the whole of the preceeding clause.
- A lot of tourists, many of whom are drunk, flood the streets of Barceloneta every day of the summer.
- A lot of cats, some of which have been abandoned,live in the street.
4. A quirky construction that you can use is…
some, any, none, all, both, either, neither, several, enough, many, few + of which / of whom / of whose
Advanced relative pronouns
As a student of advanced English grammar you also need to know the following relative pronouns. Notice their relationship with the subjunctive in Spanish.
1. Whereby = in which, by which. ‘The local council is going to end the system whereby street cleaners are paid by results instead of the hour.’
2. ‘Why’ = the reason for ‘That’s the reason why he loves you so much.’
3. Whoever, Whatever, Whichever.
- Whoever = whoever the next boss is, I’ll be a loyal employee.
- Whatever = whatever he gives his kids, they’ll be happy.
- Whichever = whichever colour he chooses, I’m sure it’ll be nice.
EXERCISE: Add – 1. Whereby, 2. whoever 3. whatever 4. whichever.
1. We’re going to introduce a new system _____________________those who want to take lunch early can do so. (1)
2. _____________________ wants to go on the excursion, can they write their name down on the list. (2)
3. Choose _____________________ style you want; all of them look good on you. (4)
4. _____________________ you do, just make sure you don’t hurt the kids. (3)
5. This whole thing _____________________ the loser has to walk home is ridiculous. (1)
6. _____________________ you choose to do, I’ll stand by you. (3)
7. That stupid arrangement _____________________ we pay the expenses is costing us too much money. (1)
8. He said the workers would be happy _____________________ was made chairman (2)
9. _____________________ team they play, Seville are bound to lose. (4)
10. _____________________ the consequences, they’re bound to be bad. (3)
11. _____________________ house they choose – flat or house – they’ll be happy. (3)
12. _____________________ he chooses – black or purple – the people will say no. (3)
13. The CEO said that _____________________ wants to be team leader has to sell 50% more. (2)
13. _____________________ becomes the next director will have to take a wage cut. (2)
14. The arrangement _____________________ guests bring their own towels is stupid. (1)
15. I think that _____________________ happens we’ll end up with a 3 degree increase in temperature. (3)
Add – 1. Whereby, 2. whoever 3. whatever 4. whichever.